1. 使用TCP发送日志
应用场景:生产中有缺少的日志或部分日志需要加入es
1.1 编辑tcp.conf
[root@linux-node2 conf.d]# cat tcp.conf
input {
tcp {
type => "tcp"
port => "6666" #监听端口
mode => "server" #server端
}
}
output {
stdout {
codec => rubydebug
}
}
#启动logstach收集tcp传过来的数据
[root@linux-node2 conf.d]/opt/logstash/bin/logstash -f /etc/logstash/conf.d/tcp.conf1.2 使用nc通过tcp向node2发送数据
[root@linux-node1 /var/log/kibana]# yum install -y nc #发送数据 [root@linux-node1 /var/log/kibana]# echo "haha" | nc 192.168.56.12 6666 #发送文件 [root@linux-node1 /var/log/kibana]# nc 192.168.56.12 6666 < /etc/resolv.conf
1.3 启动logstash,查看界面输出结果
[root@linux-node2 conf.d]# /opt/logstash/bin/logstash -f /etc/logstash/conf.d/tcp.conf
Settings: Default pipeline workers: 1
Pipeline main started
{
"message" => "haha",
"@version" => "1",
"@timestamp" => "2017-03-26T11:57:30.974Z",
"host" => "192.168.56.11",
"port" => 35944,
"type" => "tcp"
}
{
"message" => "# Generated by NetworkManager",
"@version" => "1",
"@timestamp" => "2017-03-26T11:58:29.739Z",
"host" => "192.168.56.11",
"port" => 36041,
"type" => "tcp"
}
{
"message" => "search example.com",
"@version" => "1",
"@timestamp" => "2017-03-26T11:58:29.739Z",
"host" => "192.168.56.11",
"port" => 36041,
"type" => "tcp"
}
{
"message" => "nameserver 192.168.56.2",
"@version" => "1",
"@timestamp" => "2017-03-26T11:58:29.750Z",
"host" => "192.168.56.11",
"port" => 36041,
"type" => "tcp"
}
[root@linux-node2 ~]# netstat -tunpl|grep 6666
tcp6 0 0 :::6666 :::* LISTEN 8685/java1.4 伪设备发送方式
[root@linux-node1 /var/log/kibana]# echo "hehe" > /dev/tcp/192.168.56.12/6666
{
"message" => "hehe",
"@version" => "1",
"@timestamp" => "2017-03-26T12:00:18.474Z",
"host" => "192.168.56.11",
"port" => 36216,
"type" => "tcp"
}2. rsyslog收集
logstash监听rsyslog 514端口收集日志
2.1 编辑node1上rsyslog配置文件,让rsyslog向node2 514端口传送日志
[root@linux-node1 ~]# tail -2 /etc/rsyslog.conf | head -1
*.* @@192.168.56.12:514
[root@linux-node2 conf.d]# /opt/logstash/bin/logstash -f /etc/logstash/conf.d/syslog.conf
Settings: Default pipeline workers: 1
Pipeline main started
{
"message" => "[origin software=\"rsyslogd\" swVersion=\"7.4.7\" x-pid=\"4507\" x-info=\"http://www.rsyslog.com\"] start\n",
"@version" => "1",
"@timestamp" => "2017-03-26T11:32:41.000Z",
"type" => "system-syslog",
"host" => "192.168.56.11",
"priority" => 46,
"timestamp" => "Mar 26 19:32:41",
"logsource" => "linux-node1",
"program" => "rsyslogd",
"severity" => 6,
"facility" => 5,
"facility_label" => "syslogd",
"severity_label" => "Informational"
}
......
[root@linux-node1 /var/log/kibana]# systemctl restart rsyslog
[root@linux-node1 /var/log/kibana]# logger hehe #es没索引显示多执行几次
{
"message" => "hehe\n",
"@version" => "1",
"@timestamp" => "2017-03-26T11:33:30.000Z",
"type" => "system-syslog",
"host" => "192.168.56.11",
"priority" => 13,
"timestamp" => "Mar 26 19:33:30",
"logsource" => "linux-node1",
"program" => "root",
"severity" => 5,
"facility" => 1,
"facility_label" => "user-level",
"severity_label" => "Notice"
}
{
"message" => "[euid=root]:root pts/0 2017-03-26 18:19 (192.168.56.1):[/var/log/kibana]2017-03-26 19:33:30 root logger hehe\n",
"@version" => "1",
"@timestamp" => "2017-03-26T11:33:30.000Z",
"type" => "system-syslog",
"host" => "192.168.56.11",
"priority" => 13,
"timestamp" => "Mar 26 19:33:30",
"logsource" => "linux-node1",
"program" => "root",
"severity" => 5,
"facility" => 1,
"facility_label" => "user-level",
"severity_label" => "Notice"
}2.2 编辑syslog.conf文件
[root@linux-node2 conf.d]# cat syslog.conf
input {
syslog {
type => "system-syslog"
port => 514 #字符串要用双引号引起来
}
}
output {
elasticsearch { #写入es
hosts => ["192.168.56.12:9200"]
index => "system-syslog-%{+YYYY.MM}"
}
}
#启动logstach收集rsyslog
[root@linux-node2 conf.d]# /opt/logstash/bin/logstash -f /etc/logstash/conf.d/syslog.conf
[root@linux-node2 ~]# netstat -tunpl|grep 514
tcp6 0 0 :::514 :::* LISTEN 8818/java
udp6 0 0 :::514 :::* 8818/java
#在node1上使用logger命令发送日志
[root@linux-node1 /var/log/kibana]# logger hehe
[root@linux-node1 /var/log/kibana]# logger hehe
...2.3 查看结果
3. Apache日志收集
3.1 filter grok插件使用
grok会对收集进来的事件进行过滤,字段拆分
#启动apache
[root@linux-node1 /var/log/httpd]# systemctl start httpd
#编辑grok.conf文件
[root@linux-node1 /etc/logstash/conf.d]# cat grok.conf
input {
stdin {}
}
filter {
grok {
match => { "message" => "%{IP:client} %{WORD:method} %{URIPATHPARAM:request} %{NUMBER:bytes} %{NUMBER:duration}" }
}
}
output {
stdout {
codec => rubydebug
}
}
#查看结果
[root@linux-node1 ~]# /opt/logstash/bin/logstash -f /etc/logstash/conf.d/grok.conf
Settings: Default pipeline workers: 2
Pipeline main started
55.3.244.1 GET /index.html 15824 0.043
{
"message" => "55.3.244.1 GET /index.html 15824 0.043",
"@version" => "1",
"@timestamp" => "2017-03-26T12:26:35.731Z",
"host" => "linux-node1.example.com",
"client" => "55.3.244.1",
"method" => "GET",
"request" => "/index.html",
"bytes" => "15824",
"duration" => "0.043"
}grok插件缺点:
grok正则匹配影响机器性能
不灵活,除非很懂ruby
生产中建议使用python脚本做正则过滤:
logstash --> redis --> python脚本(多进程) --> es
3.2 收集apache日志
[root@linux-node1 /etc/logstash/conf.d]# cat apache.conf
input {
file {
path => "/var/log/httpd/access_log"
start_position => "beginning"
}
}
match => { "message" => "%{COMBINEDAPACHELOG}" }
}
}
output {
elasticsearch
filter {
grok { {
hosts => ["192.168.56.11:9200"]
index => "apache-access-log-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
[root@linux-node1 /etc/logstash/conf.d]# /opt/logstash/bin/logstash -f /etc/logstash/conf.d/apache.conf
Settings: Default pipeline workers: 2
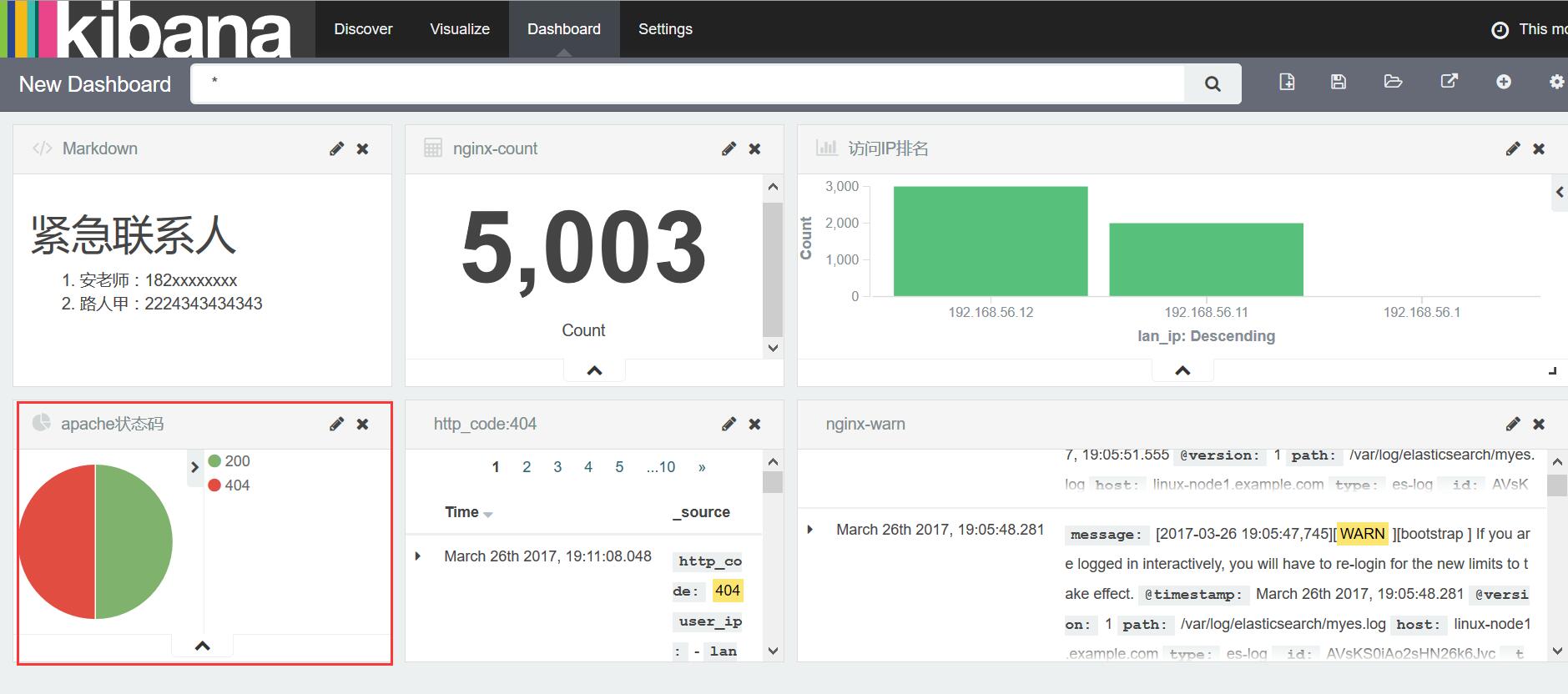
Pipeline main started3.1 查看结果,饼图显示
[root@linux-node1 ~]# ab -n 1000 -c 1 http://192.168.56.11/ [root@linux-node1 ~]# ab -n 1000 -c 1 http://192.168.56.11/dffdf